
( F) Real-time place-preference data show tracks of control (left) and ZI VGAT-ChIEF mouse (right) in photostimulation-paired (photostim.) and nonpaired chambers. ( E) Light-dark conflict test shows photostimulation increases high-fat food intake in brightly lit chamber. ( D) Photostimulation increases time in lit chamber during light-dark conflict test. ( C) Latency of feeding initiation using 10-s photostimulation (10-ms pulses) at 10, 20, and 40 Hz. Photostimulation protocol same as in (A). ( B) Latency for representative mouse to rapidly initiate feeding in response to photostimulation over 30 consecutive trials. ( A) Photostimulation of ChIEF-expressing ZI axons reduces activity of PVT glutamate neuron in brain slice during repeated 10-s photostimulations (10 ms, 20 Hz) with 30-s rest interval. Statistical analysis for comparison between two groups: two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc comparison for (E) and (J) unpaired t test for (G) one-way ANOVA repeated measure with Bonferroni post hoc comparison for (H) two-way ANOVA repeated measure with Bonferroni post hoc comparison for (I) and (K). ( K) Bic attenuates optogenetic stimulation of food intake in PVT. For 4 ×10-min trial, 10-min light stimulation (10 ms, 20 Hz) followed by 30-min no stimulation, repeated four times. ( J) Food intake for 24 hours with photostimulation of ZI VGAT neurons or VGAT ZI-PVT terminals. ( I) VGAT ZI-PVT photostimulation increased preference for high-fat food. ( H) Food intake induced by photostimulation is greater in first 10-min trial, and reduced in second and third trial, with a 5-min interval between photostimulations. ( G) Cumulative time during eating by VGAT-ChIEF mice during 10-min photostimulation (10 ms, 20 Hz). ( F) Photostimulation of PVT has no effect on food intake of VGAT-Cre mice after control AAV-tdTomato injection into ZI. ( E) Photostimulation (10 ms, 20 Hz) of ZI-VGAT-ChIEF neuron terminals in PVT increases food intake during 10-min trial. In bicuculline (Bic, 30 μM), 1-Hz pulses evoked no obvious current. ( D) Optogenetically evoked inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) of PVT vGlut2 neurons at 1, 5, 10, and 20 Hz (membrane potential clamped at −40 mV). ( C) RV-labeled presynaptic neurons in ZI. (Bottom) PVT neurons detected with TVA-mCherry (left), RV-GFP (middle) and merged image (right) shows originating cells (yellow, expressing both GFP and mCherry). (Top right) Selective expression of RV-GFP (green) and TVA-mCherry (red) in PVT. TVA, the avian tumor virus receptor A RV dg, glycoprotein–deleted rabies virus (RV).
(Top left) Schematic shows the strategy for tracing presynaptic ZI projections to PVT glutamate neurons. ( B) Retrograde mapping of presynaptic neurons to PVT glutamate neurons. (Bottom left) Red fluorescent image shows strong projection to PVT from ZI-VGAT-ChIEF-tdTomato neurons. (Top left) Schematic shows bilateral injection of AAV-ChIEF-tdTomato into ZI and placement of fiber optic tip above PVT. ( A) Anterograde mapping of ZI GABA neuron projections to PVT. Statistical analysis for comparison between two groups: Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post hoc comparison for (D) and (E) unpaired t test for (G), (I), (L) and (M). ( M) Ghrelin increases the firing rate of ZI GABA neurons. ( L) Ghrelin depolarizes ZI GABA neurons. ( K) Ghrelin (100 nM) excites a ZI GABA neuron. ( J) EPSC amplitude from ZI GABA neurons in mice fed ( n = 12 cells from four mice) or mice fasted for 24 hours ( n = 13 cells from four mice). ( I) EPSC frequency from ZI GABA neurons of mice fed ( n = 12 cells from each of four mice) or mice fasted for 24 hours ( n = 13 cells from four mice). ( H) Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in ZI GABA neurons of mice fed or fasted for 24 hours.

( G) Firing rate at different levels of current injection from ZI GABA neurons in brain slices of mice fed or fasted for 24 hours. ( F) Action potentials evoked by 100-pA current injection in ZI GABA neurons in brain slices of mice fed or fasted for 24 hours.
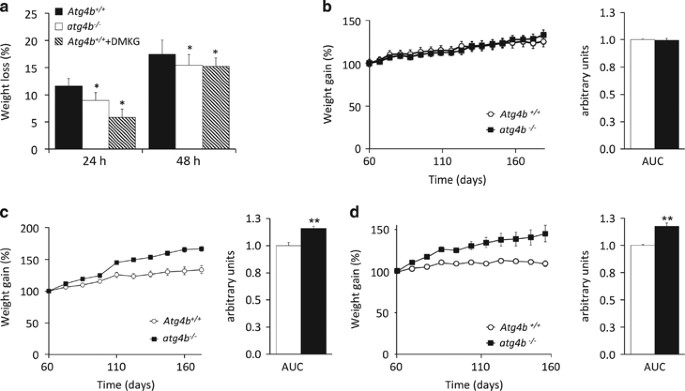
#Ablation and weight gain 2017 trial#
( E) High-fat food intake over 10 min and four times 10-min trial as a percentage of unstimulated 24-hour intake (100%).

For the 4 ×10-min trial, 10-min light stimulation (10 ms, 20 Hz) was followed by 30 min without stimulation, repeated four times. For the 10-min trial, continuous light stimulation (10 ms, 20 Hz) was supplied to the ZI. ( D) High-fat food intake during 10 min and four times 10 min from control mice with tdTomato and mice with ChIEF-tdTomato, both with ZI expression. ( C) Schematic illustration showing the location of optical fiber tips implanted above the ZI on both sides of the brain. ( B) Optogenetic activation with varying frequency of a ZI GABA neuron in a brain slice. (A) Red fluorescent image shows restricted expression of ChIEF-tdTomato in the ZI after AAV-ChIEF-tdTomato was bilaterally injected into the ZI of VGAT-Cre mice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
